Essential Laser Beam Parameters To Know About Your Laser System
If you shine a laser and look very closely at its laser spot, you’ll see that certain regions are more brightly lit than others.
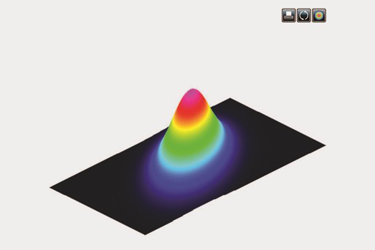
Exactly how the laser’s intensity is distributed is what we call the beam profile, which can be viewed with a laser beam profiling camera such as this one:
Flat-Top Lasers
The laser is either on or off, with a clear boundary in between. No gray areas.
This is good for certain applications, however, flat-top beams do not stay well-defined when propagating. Flat-top lasers combine multiple wavefronts, which get out of sync as the laser travels, hence a blurrier profile.
Gaussian Lasers
An ideal Gaussian laser beam profile will have an intensity distribution like a bell curve (i.e. a Gaussian distribution). The M2 factor indicates how closely the beam resembles a perfect Gaussian.
Gaussian beams provide these notable advantages:
- Profile is preserved as it propagates
- Tightest possible focusing
- Lowest beam divergence
- Cost-efficient
Irregular
The name says it all.
These beam profiles are either completely irregular, or approximately Gaussian/flat-top, but with hotspots.
Get unlimited access to:
Enter your credentials below to log in. Not yet a member of Photonics Online? Subscribe today.
