Early Non-Invasive Visualisation And Characterisation Of Vascular Disease
Andor Neo sCMOS camera answers need for fast frame rate in novel retinal imaging technique
As well as allowing us to image the world around us, the eye offers clinicians a deep and immediate insight into the condition of our vasculature. Abnormalities in the retinal vasculature have been correlated with a diverse range of conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, migraine, and glaucoma, and several techniques have become established to measure blood flow in the human retina.
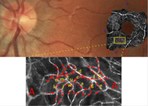
However, the earliest anomalies in vascular disease arise in the microvasculature and current imaging methods lack the spatiotemporal resolution to track blood flow at the capillary level. Now, an Australian team has used the high sensitivity and fast frame rate capability of Andor’s Neo sCMOS camera to demonstrate direct, non-invasive optical imaging of erythrocyte flow in human retinal capillaries and validate its use as an investigative tool for early signs of disease.
Led by Phillip Bedggood and Andrew Metha, the group modified an ophthalmoscope with adaptive optics to achieve a 1.5 micron spatial resolution and a flood illumination system. The Neo sCMOS camera replaced the previous CCD camera and was used to gather data at up to 460 frames per second. When tested on the eye of a human subject, the range of erythrocyte velocities was found to be in agreement with previously published figures based on retinal leukocytes.
According to Phillip Bedggood, “We evaluated a number of cameras from various manufacturers before selecting the 5.5 Megapixel Andor Neo, which offered the specifications we were looking for and a competitive price. It was quite simple to replace the CCD camera with the Neo. The camera head itself and the framegrabber were both supplied by Andor together with an SDK and a simple to use interface. This lessened software teething issues that we have faced in the past and meant we could quickly make use of the Neo’s fast frame rate capabilities and large field of view.”
“Phillip Bedggood’s work is highly significant,” says Orla Hanrahan, Application Specialist at Andor. “In directly visualising red blood cells in the retinal capillaries they can now use this approach to study the dynamics of the retinal vascular supply under normal conditions and in response to functional stimulation of the retina. More importantly, they will be able to investigate how the dynamics change in the presence of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases, such as diabetes, stroke, and Alzheimer’s.”
Andor’s Neo sCMOS camera is unlike any CMOS or CCD detector, setting radical benchmarks with its unique ability to simultaneously deliver the highest specifications in sensitivity, resolution, speed, dynamic range, and field-of-view. The Neo sCMOS represents true, no-compromise scientific imaging within a ‘mid-range’ price bracket and is ideally placed to become the new gold-standard, workhorse imaging detector. The Neo sCMOS is suitable for a broad range of high resolution and microscopy applications, including wide field fluorescence microscopy, calcium ratio imaging, FRET, and TIRF. To learn more about the Neo sCMOS camera, please visit the Andor website [http://www.andor.com].
Reference
1. Phillip Bedggood and Andrew Metha “Direct visualization and characterization of erythrocyte flow in human retinal capillaries,” Biomedical Optics Express Vol. 3, No. 12, 3264-3277 (2012)
About Andor
Andor is a world leader in Scientific Imaging, Spectroscopy Solutions and Microscopy Systems. Established in 1989 from Queen's University in Belfast, Northern Ireland, Andor Technology now employs over 300 people in 16 offices worldwide, distributing its portfolio of over 70 products to 10,000 customers in 55 countries.
Andor’s digital cameras, designed and manufactured using pioneering techniques developed in-house, allow scientists around the world to measure light down to a single photon and capture events occurring within 1 billionth of a second. This unique capability is helping them push back the boundaries of knowledge in fields as diverse as drug discovery, toxicology analysis, medical diagnosis, food quality testing and solar energy research. For more information, visit http://www.andor.com.
Source: Andor Technology plc.
